While most women understand they should begin prenatal vitamins before conception, and really the day they decide that they want to try for a baby, preconception advice for men isn’t quite as well known. But like women, men really do benefit from specialized nutrition in the form of a prenatal vitamin that’s formulated to support sperm health. Here’s what that looks like, and how specific nutrients can impact a man’s fertility health before fatherhood.
Key Takeaways
- Male prenatal vitamins or fertility supplements can support sperm health, which may improve your chances of conceiving and improve pregnancy and infant health outcomes.
- While men should take prenatal vitamins, their needs are different than women’s, which means they won’t benefit from a women’s prenatal vitamin.
- Men should look for a male prenatal vitamin that contains zinc, folate and key antioxidants.
- In addition to a daily prenatal vitamin, men will also benefit from a nutrient-dense diet, consistent exercise, stress management and sufficient sleep.
What Does a Men’s Prenatal Vitamin Do?
The general assumption is that a woman takes prenatal vitamins to support early fetal health and development. While that’s true, it’s an incomplete assessment. Prenatal vitamins taken at least three months before conception actually help prepare the body for pregnancy, and that’s true for men, too. A men’s prenatal vitamin includes ingredients that support sperm production, sexual function and hormonal balance. Science has made clear that the health of a man in the three to four months before conception has a direct effect on his partner’s ability to conceive and the health of the pregnancy, so this is no small thing (1). What’s more, inferior sperm quality is pretty darn rampant, with studies confirming falling sperm concentrations around the globe. Concentration is one parameter of sperm health, which also includes:
- Sperm morphology, or the shape and the size of the sperm. Abnormal sperm are associated with lower fertility rates, and poor sperm morphology is linked to poor lifestyle habits.
- Sperm motility, or is how well sperm swim. A man is considered fertile if 40% of his sperm are motile.
Decades of research show us that the right vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can support all of these sperm health parameters, as well as the quality of the DNA in sperm (2).
Which Nutrients Do Men Need Before Conception?
According toDr. Darren Bryk, andrology/male fertility fellow at the University of Virginia, “Anything a man can do to improve his overall health–eating healthy, staying active, avoiding cigarette smoking–can improve a man's fertility potential.” Nutrition is also high on the list, and since even the most mindful diet has gaps, supplementing with a prenatal vitamin can help ensure men are getting the right nutrients in the right amount. That includes specific vitamins, minerals and antioxidants.
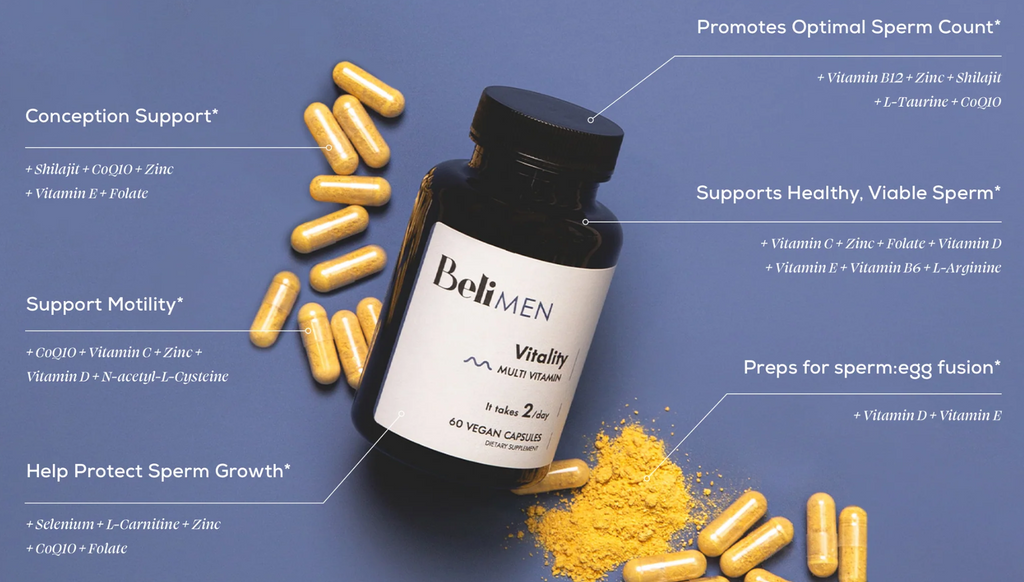
CoQ10
This antioxidant has been shown to support sperm motility and fertilization rates (3).
Methylated folate
A form of vitamin B9, methylated folate is associated with better sperm concentration and quality (4). And if you’re wondering about the difference between folate and folic acid, or how 5-MTHF fits into this, we have an entire post on the topic.
Vitamins C, E, B6, and B12
These antioxidants support sperm quantity, motility, and morphology (5). They also help protect sperm from free radical damage. They also complement other key antioxidants, such as CoQ10 and selenium.
Vitamin D
Supplementing with this hormone is linked to improved sperm quality (6). And yes, it’s true sun exposure is the best way to get vitamin D, but most of us don’t get enough sun to ensure an adequate amount of vitamin D. That's where supplementing comes in.
L-Carnitine
This amino acid derivative has been linked to higher fertilization rates and better quality sperm (7).
Selenium
This antioxidant can boost testosterone and help improve sperm across multiple parameters (8). In combination with vitamins A, E, or C, selenium has been shown to increase sperm quality overall.
N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine
This antioxidant may help improve sperm count, motility, and morphology.
L-Arginine
This amino acid is required for quality sperm production (9).
L-Taurine
This antioxidant helps support men's health.
Zinc
Zinc is an essential mineral linked to improved sperm motility, functional sperm morphology and higher sperm volume (10).
Shilajit
This Ayurvedic adaptogen helps promote sperm count, motility, and serum testosterone.
All of these nutrients are included in Beli Vitality for Men, a scientifically-aligned men’s prenatal supplement that uses bioavailable ingredients in effective amounts.
What Else Can A Man Do To Increase His Chances of Conception?
Of course, a prenatal vitamin alone isn’t all a man should do to improve his health before conception. If you’re thinking of starting a family, cleaning up your lifestyle is an important first step. That includes committing to regular exercise, getting plenty of sleep, finding healthy outlets to manage stress, cutting back on alcohol, caffeine and recreational drug use, and generally embracing all the tenets of a healthy lifestyle. A sperm analysis may also offer some baseline information about the current state of your sperm health. Pairing these steps with a daily men’s prenatal vitamin can help nourish a man’s preconception health for the best chances of fatherhood.
Article Resources
- Preconception Health. (2018). https://www.thelancet.com/series/preconception-health
- Cetin, I et al. (2010). Role of micronutrients in the periconceptional period. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19567449/
- Vishvkarma R et al. (2020). Coenzyme Q10 effect on sperm parameters: profound or meagre? https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/and.13570
- Boxmeer J et al. (2009). Low folate in seminal plasma is associated with increased sperm DNA damage. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18722602/
- Colagar, A et al. (2009). Ascorbic acid in human seminal plasma: determination and its relationship to sperm quality. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2735625
- Ahmadi S et al. (2016). Antioxidant supplements and semen parameters: an evidence-based review. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28066832/
- Wu, Z et al. (2012). Short-term medication of L-carnitine before intracytoplasmic sperm injection for infertile men with oligoasthenozoospermia. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22474993/
- Moslemi M et al. (2011). Selenium–vitamin E supplementation in infertile men: effects on semen parameters and pregnancy rate. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3048346/
- Stanislavov R et al. (2014). Sperm quality in men is improved by supplementation with a combination of L-arginine, L-citrullin, roburins and Pycnogenol®. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25531191/
- Wong W et al. (2002). Effects of folic acid and zinc sulfate on male factor subfertility: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11872201/